Intel, once the uncontested titan of semiconductors, has undergone significant restructuring over the past decade in a bid to restore its competitive edge and profitability. Among the most dramatic of these moves has been a series of large-scale workforce reductions. In this blog, we examine whether these aggressive layoffs have delivered the intended positive impact on Intel earnings, digging into the numbers and underlying trends.
1. Intel’s Layoff Timeline: An Overview
Intel reduced its workforce in several waves:
- 2023–2025: Most notable rounds, with approximately 15% of employees cut annually in 2024 and 2025(ongoing). Headcount expected to drop from nearly 125,000 to 75,000.
- Early 2020s: Several smaller layoffs and efficiency pushes, generally less than 5% of employees at a time.
These layoffs were part of broader cost-cutting drives, amid declining market share and intense competition from AMD and Nvidia.
2. The Rationale: Why Cut Jobs?
Intel’s leadership repeatedly cited the need to reduce expenses, streamline management, and fund future technology bets as reasons for job cuts. The goal was simple: improve margins and return to profitable, revenue-generating growth after years of stagnation and strategic missteps which will eventually improve Intel earnings.
3. The Earnings Record: What Do The Numbers Say?

Let’s examine key data from Intel’s most recent and substantial layoff periods, focusing on the financial impact.
Table: Intel Annual Employee Count (2020–2025)
| Year | Workforce (End-Q2) | Revenue (B USD) | Net Income/Loss (B USD) | EPS (USD) | Major Layoffs? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | ~110,600 | 19.7 | 5.1 | 1.19 | No |
| 2021 | ~121,100 | 19.6 | 5.1 | 1.19 | No |
| 2022 | ~131,900 | 15.3 | 1.0 | 0.25 | No |
| 2023 | ~124,800 | 12.9 | -1.6 | -0.41 | Minor |
| 2024 | ~108,900 | 12.8 | -1.6 | -0.43 | Yes (15%) |
| 2025(proj) | ~75,000 | 12.8 | -2.9 | -0.77 | Yes (15%) |
Note: 2025 numbers reflect projections and reported ongoing mass layoffs but will be finalized at year-end.
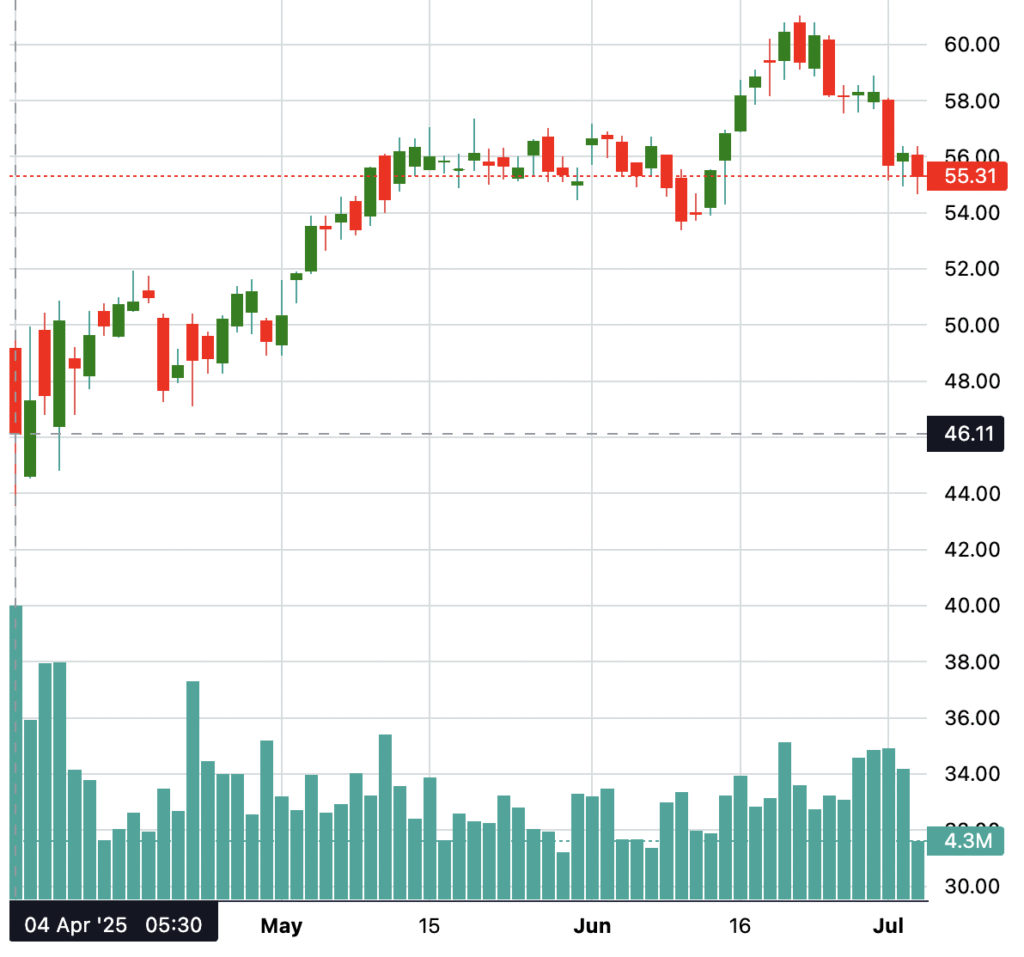
Immediate Impact on Intel earnings
- 2024–2025 Losses: Despite headline-grabbing layoffs, Intel’s net losses expanded: from -$1.6B in Q2 2024 to -$2.9B in Q2 2025. EPS also worsened.
- 2025 Charges: Layoffs and restructuring accounted for $1.9B in charges in Q2 2025 alone—swamping any labor cost savings realized during the period.
- Revenue Plateau: Revenue remained flat at $12.8–$12.9B, suggesting that layoffs failed to jumpstart growth .
Market Reaction
Intel’s stock rose modestly (about 3%) on initial layoff announcements, reflecting optimism about eventual cost savings, but shares quickly reversed course as earnings reports showed continued losses and one-time charges absorbed any savings.
4. Precedents: Earlier Layoffs and Financial Performance
Intel periodically trimmed its workforce over the last decade—but smaller reductions in the early 2020s also failed to manifest as clear profit growth or competitive resurgence.
- 2016–2019: Workforce reductions and a series of restructurings produced short-term cost savings but did not reverse slumping margins or market share loss.
- 2020–2022: Despite holding steady or modestly reducing staff, Intel saw sharp drops in profit as R&D underinvestment and tough competition sapped growth.
5. Why Didn’t Layoffs Spur Profitability?
Several factors explain the lack of immediate lift in Intel earnings:
- Restructuring Costs: Each major layoff resulted in large one-time expenses—$1.9B in Q2 2025—directly dragging down quarterly earnings.
- Top-Line Pressure: Intel’s fundamental problem has been stagnant or falling sales. Even as employee costs dropped, flat revenues meant savings failed to translate into net profit .
- Competitive Weakness: The loss of market share to AMD, Nvidia, and new AI chipmakers limited the upside from cost controls. Real profitability gains require robust top-line growth or margin expansion—neither of which layoffs alone could produce.
- Talent Drain and Disruption: Large layoffs can harm culture, morale, and productivity, compounding execution risks during an attempted turnaround.
6. The Longer View: Can Layoffs Ever Help?
Intel’s management insists that cost-cutting—including layoffs—lays the groundwork for a leaner, stronger company. Indeed, workforce reductions can boost margins and profitability if matched with revenue stabilization and improved competitive positioning. However, as the past several years show, layoffs alone—especially amid sagging sales and heavy restructuring costs—do not deliver immediate, data-backed growth in Intel earnings.
7. Conclusion: Layoffs Offer No Quick Fix
The evidence is clear: layoffs over the past five years have not produced positive, immediate impacts on Intel earnings. Substantial one-time charges erased near-term savings, while ongoing revenue pressures meant that earnings continued to deteriorate despite a much smaller workforce. Only with sustainable top-line improvement and a proven roadmap rebound can cost reductions translate into real profit gains.
For now, the layoff story at Intel serves as a cautionary tale: cost cuts alone are not a panacea, and effective turnaround demands a holistic focus on both expenses and growth engines.
References:
Q2 2024–2025 Intel earnings press releases and SEC filings.
Financial data and layoff coverage from Reuters, Bloomberg, and major financial news outlets.
Disclaimer:
The data and information presented in this blog are sourced from third-party providers and are for educational and informational purposes only. We do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or authenticity of this data. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Always perform your own due diligence and consult with a licensed financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Use this information at your own risk.